- Upon arrival, pharmaceutical products are inspected for any damage or discrepancies.
- Quality control checks are performed to verify the integrity of the original packaging and product.
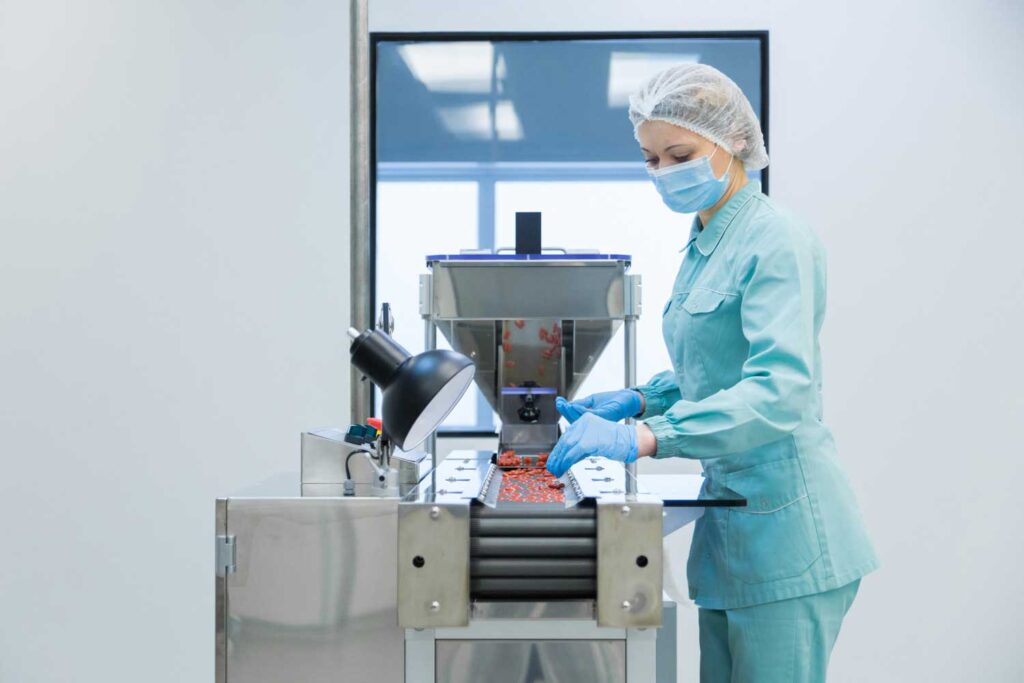

Repacking pharmaceutical products is a core element of MIBEMA daily operations involves transferring medications from their original packaging into new packaging, often to meet specific regulatory requirements, improve usability, or tailor products for particular markets.
This process must be conducted with utmost care to maintain the integrity, efficacy, and safety of the medications.
and regulations vary by region. Repacking ensures that products comply with local labeling requirements, language standards, and packaging regulations, facilitating their safe and legal distribution in different markets.
Repacking allows pharmaceutical companies to customize packaging for different markets, addressing specific needs such as dosing instructions, branding, and patient information. This customization can enhance patient adherence and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
Repacking can make medications easier to use by providing more user-friendly packaging solutions. For example, blister packs, single-dose units, and child-resistant packaging can enhance convenience and safety for patients.
Repacking can optimize supply chain operations by reducing packaging bulk, improving storage efficiency, and facilitating distribution logistics. This efficiency can lead to cost savings and faster delivery times.
Maintaining the highest quality standards is crucial in the repacking process. Every step, from opening the original packaging to sealing the new one, must be conducted in a controlled environment to prevent contamination and ensure the product's integrity.
Comprehensive documentation is essential to ensure traceability and accountability. This includes recording batch numbers, expiration dates, and repacking dates. Proper documentation helps in tracking the product’s journey from the manufacturer to the end-user, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.

Accurate labeling is critical to avoid medication errors. Labels must include essential information such as the drug name, dosage, administration instructions, expiration date, and any warnings. Inaccurate labeling can lead to serious health risks and regulatory penalties.
Repacking facilities must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory guidelines set by authorities such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO. Compliance ensures that repacking operations meet the required safety and quality standards.

To prevent counterfeiting and ensure the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, repacking operations should incorporate security features such as tamper-evident seals, holograms, and unique identifiers. These measures help protect patients and maintain the integrity of the supply chain.
Distribution
Repacked products are stored and distributed according to standard operating procedures, ensuring they reach the end-users in optimal condition.
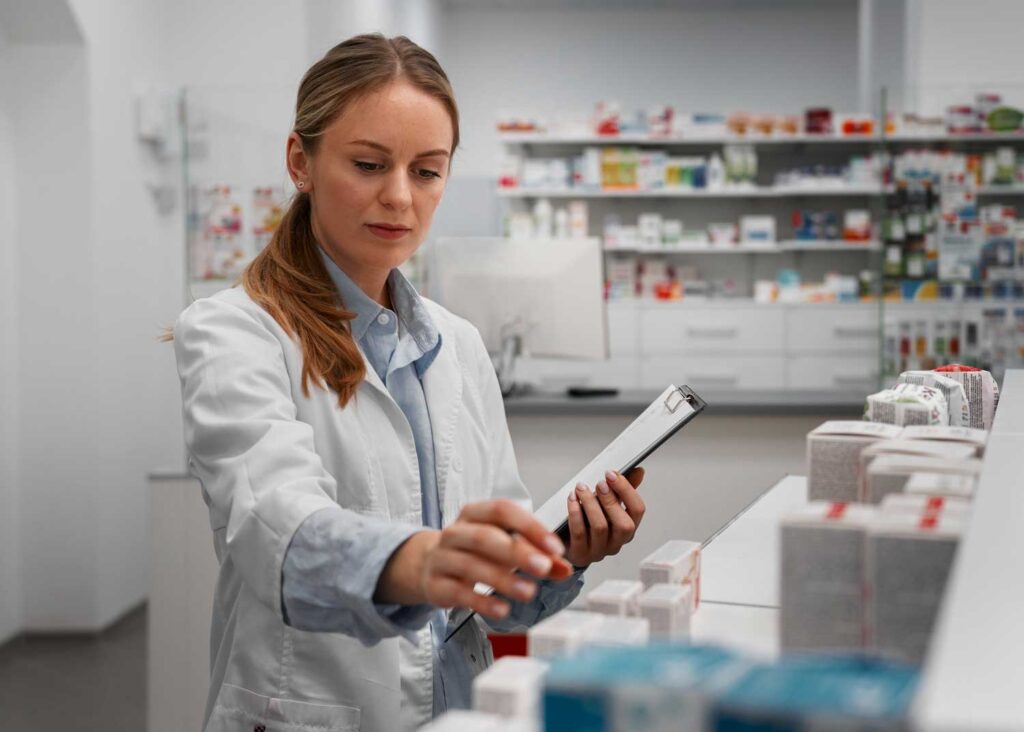

Repacking pharmaceutical products is a critical process that requires meticulous attention to detail and strict adherence to regulatory standards. By ensuring quality, accuracy, and compliance, repacking helps pharmaceutical companies meet market demands, improve patient safety, and enhance the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the role of repacking will remain essential in delivering safe and effective medications to patients worldwide.